Building a Bot For a Travel Website
This project focuses on using the Botpress service to test the capabilities of a customer service bot in providing relevant and accurate tourism resources.
You can test out the bot here.
A tourism website promoting Banff and Waterton National Park was built to embed the bot. The bot was designed to assist users by answering questions about the parks activities, accomodation, and trails. When building the bot I ran into the issue of not knowing where the tourism information was source from. To remedy this I designed the bot to source all of its responses from a knowledge base consisting of official tourism websites for Banff and Waterton National Park. Another issue resolved was providing a direct link for tourism information. To accomplish this the bot was programmed to searche for any phrases containing the words "link to" in order to provide a hyperlink to Banff and Waterton resources exclusively.
Additionaly, I wanted to test the bot's ability to facilitate bookings. For this, I created a simple reservation system for an italian restaurant.
I wanted to test the bot's ability to handle tasks such as reserving a table at the restaurant, editing a reservation, and providing a filterable menu.
For the reservation interface the bot looks for when the phrase "book a reservation" is typed in the chat window.
The user is then shown these options:
-
Make a new reservation. This asks for the user's date of reservation, email address, and number of people. A confirmation email is then sent containing this info and the reservation number to cancel/change reservation.
-
View or modify reservation: Provide the confirmation number in the email sent to view or modify current resrvation.
-
Cancel reservation: To cancel the user needs to provide the confirmation number. This number is in the email sent to the user.
-
Learn about the menu: View the full menu. Users can ask for reccomended dishes and filter by price or dietary restrictions.
Variables were created in Botpress to store reservation information such as for the confirmation number, date and time, email, and party size. This information is stored in a reservation table. The table is updated whenever users delete or modify their reservation.
Through this project, I was able to assess how well the bot could interact with users, provide accurate tourism information, and manage reservation information.
More Information About Setting Up and Using Botpress
Botpress Overview
Botpress is a platform to build AI agents using a variety of LLMs and integrations with other software.
Setting Up the First Bot
For users new to Botpress they can have Botrpess create a basic bot for them.
First create create a free account on the website. Next click "Create new chatbot" option on the homepage.
Pick the menu option for creating a first time chatbot. This is a guided process where you follow on screen instructions.
Users select the:
- The chatbot name.
- Where is the chatbot getting data from. You can provide various links and company names to pull information from.
- Which chatbot agents to include. Summary, translation, analytics, personality agents were chosen.
- Adjust the starting knowledge base. The knowledge base is where the bot is accesing information from when providing responses. Users can restrict information access to specific websites and files (pdf, plain text).
When finished the initial setup click the publish button to create your first bot.
The appearance of the bot can be adjusted in the webchat tab located on the left sidebar.
You can adjust the name, description, the theme (color, font). When using the bot elsewhere you can get a link or embed code for a personal website. The code is an embed code pasted under the body tag. After embedding the chatbot on your website refresh the page to run the bot. The chatbot should show as a icon widget on the bottom irght side of the webpage.
Botpress Interface
Menu Bar (Left Column)
The menu bar on the left column provides access to various features of the bot interface.
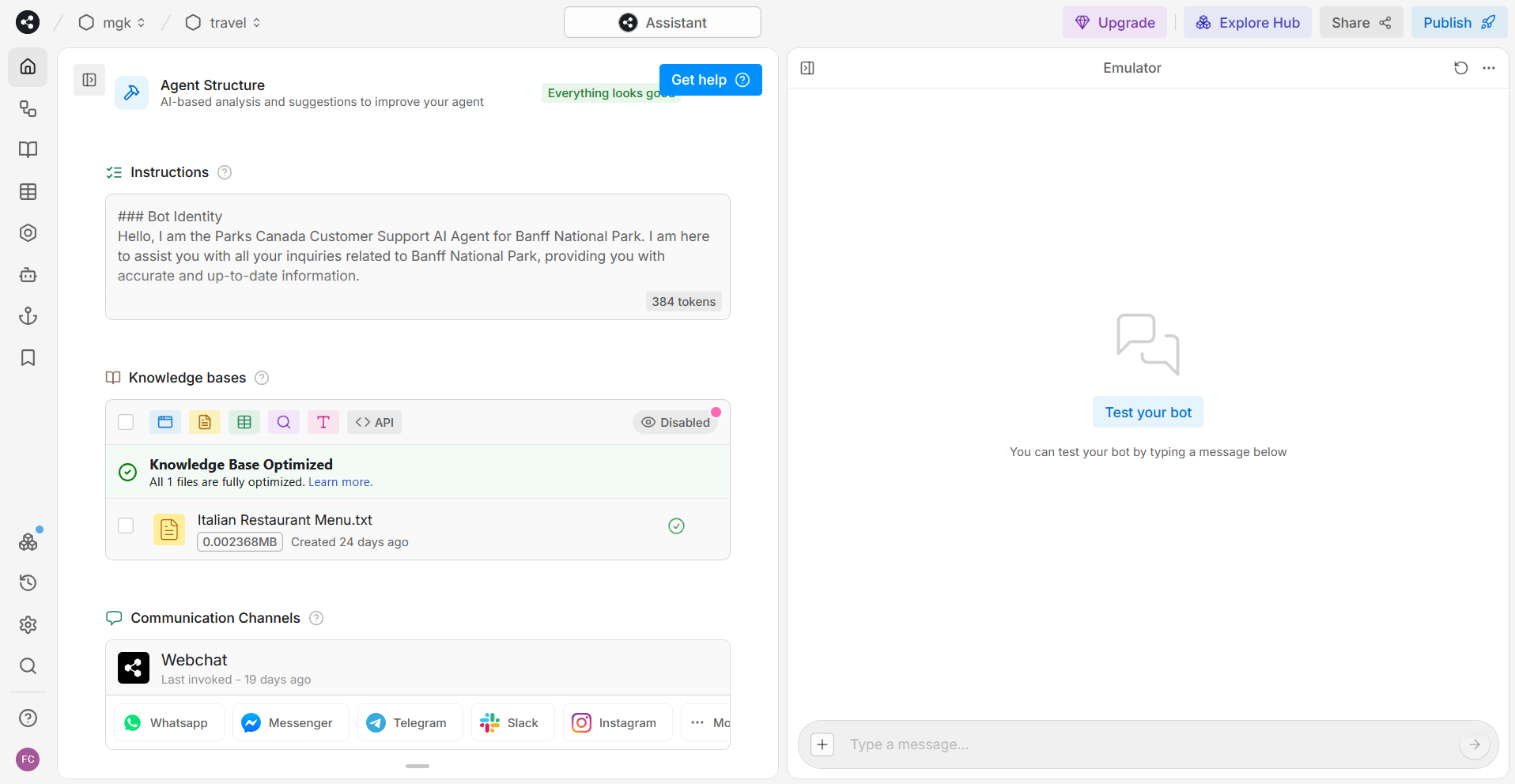
Home
The home section includes the name of the chatbot, a description of its functionality, and a set of instructions. These instructions define the bot's identity, its scope and responsibility, the greeting message on startup, the response style, capabilities, and any applicable policies.
Search
This section enables you to search for or filter information related to the bot's knowledge bases.
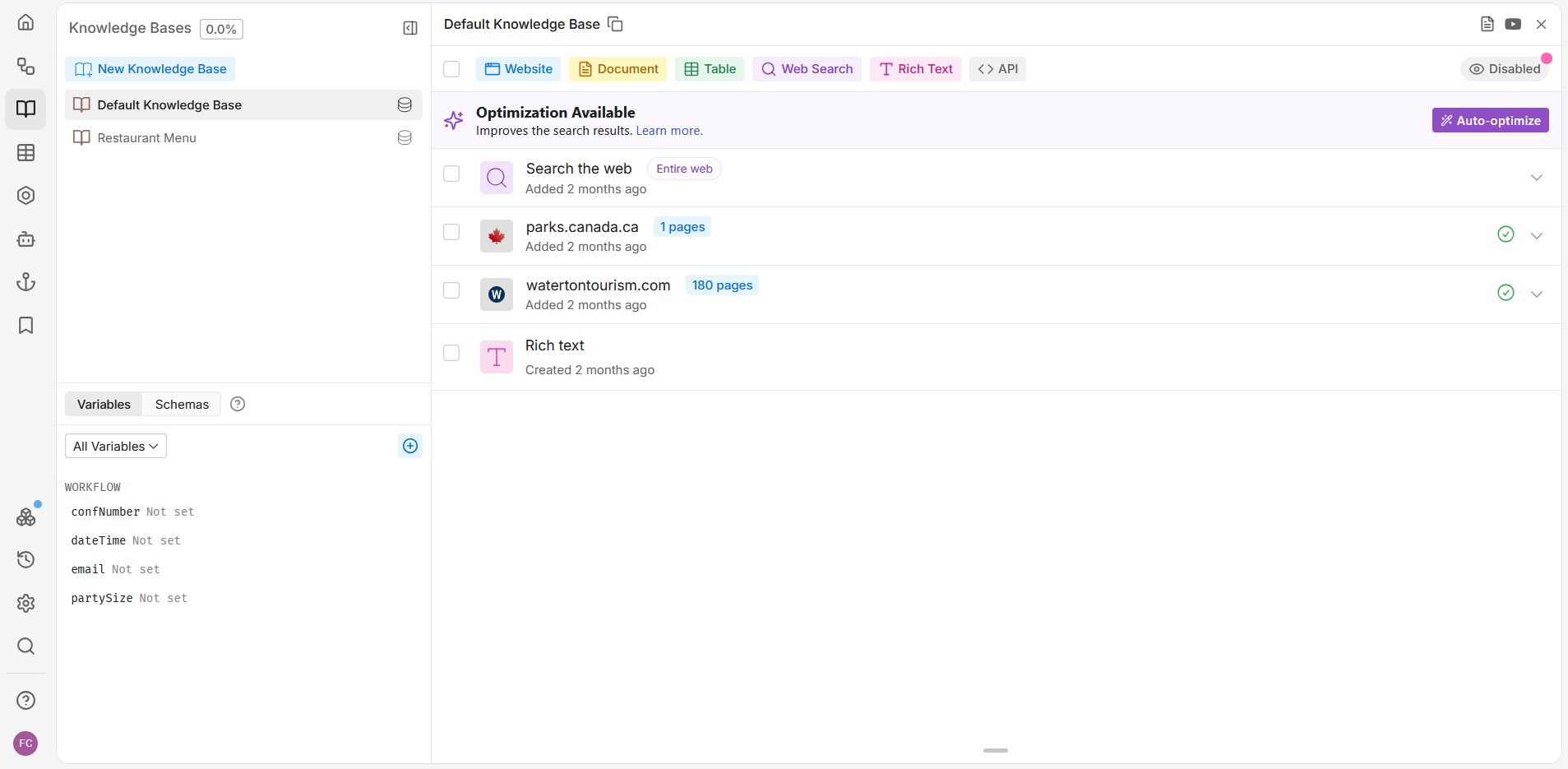
Knowledge Bases
Defines where the bot retrieves its information from. For example, it could be from a text file, web searches, or tourism websites.
Tools
This section lists the actions the bot can perform. For example, the bot may conduct a web search of official Banff or Waterton tourism websites, provide links to tourism sites, and offer reservation options.
Channels
The channels section shows the enabled communication channels, such as web chat.
Agents
Lists agents that enhance the bot's capabilities. Agents may perform tasks like summarizing conversations, providing analytics, or translating text.
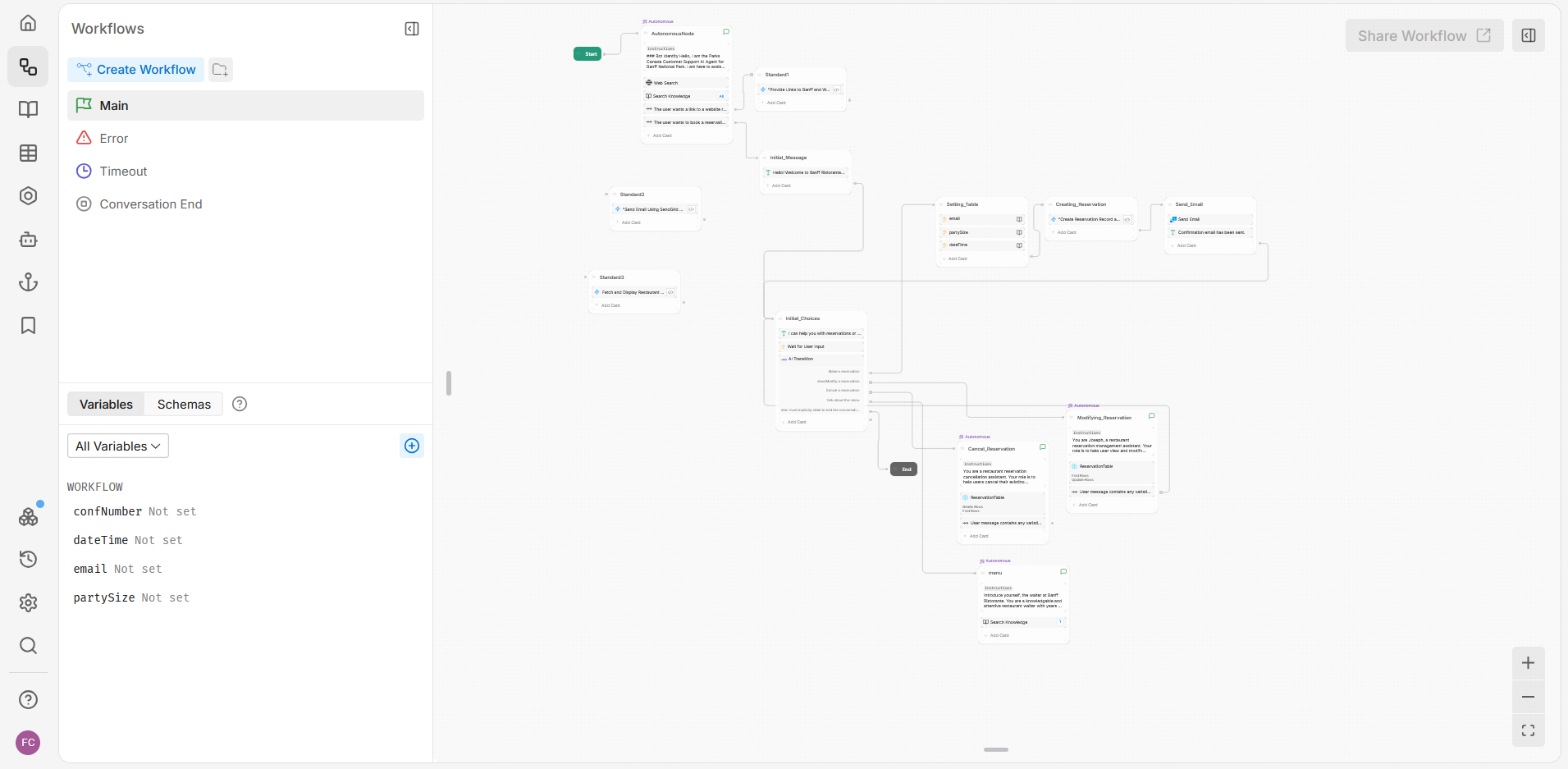
Workflows
This section allows you to manage the flow of the conversation. It includes flow chart diagrams with connected nodes representing the bot's logic. Nodes contain tasks like sending messages (text, image, audio, or video), executing code, or managing data tables.
Types of Nodes
- Standard Node: A versatile building block in the bot's workflow. It allows for both instructions and transitions to other nodes.
- Autonomous Node: Uses an LLM to determine the flow and actions based on the conversation's context.
- Start Node: The entry point for the main conversation flow.
- Entry Node: The start of each workflow, apart from the main flow, defining conditions for execution.
- Exit Node: Marks the end of a workflow, typically with cleanup or finalization actions.
- End Node: Resets the conversation session and clears data in the main flow.
Variables
This section tracks user interactions and stores data for later use, visible in the bottom left corner.
Knowledge Bases
Specifies where the bot retrieves its information, including sources like websites, documents, tables, web searches, and APIs.
Tables
Contains a local database for storing information, such as reservation details, and includes a default conversation table for storing summaries and transcripts.
Actions
Allows for the creation of custom, reusable code actions. These can be used in workflows, hooks, capabilities, and tables.
Hooks
Hooks enable customization of the bot's behavior by executing code at specific points. They allow interception and modification of messages, session management, logging, and integrations with external systems.
Library
This feature is deprecated as of April 2025.
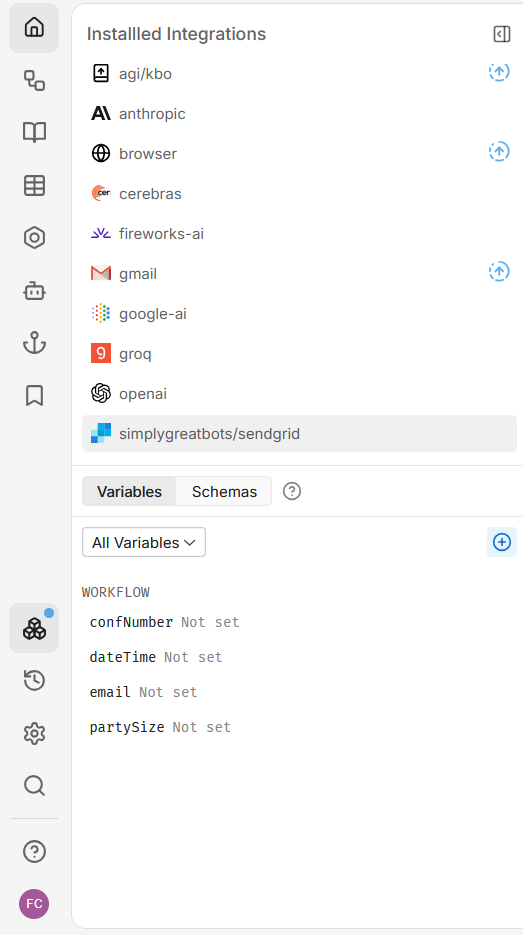
Integrations
Displays the integrations currently installed on your bot, such as SendGrid for email notifications.
Versions
Allows you to view, compare, and revert to previous versions of your bot.
Bot Settings
Adjust various settings, including the bot's name, the LLM used, timeout options, and client settings.
Search
A search function for finding specific settings or information.
Help (Resources)
Provides access to documentation, quick references, and status updates for support.
User Preferences
Allows customization of viewing options, such as light/dark mode, grid snapping, and toggling the bot home page section on or off.
Content (Middle Column)
This section contains the content displayed for the user.
Botpress Emulator (Right Column)
The Botpress emulator on the right column allows for bot testing by messaging. It provides options to refresh the conversation, start as a new user for training, and publish new versions of the bot.
Botpress Agents
Agents are specialized components that enhance a bot's capabilities by performing specific tasks to improve user interaction, information retrieval, and conversation management.
Summary Agent
- Summarizes conversation transcripts to provide a transcript that can be embedded in prompts.
Personality Agent
- Customizes the chatbot's personality, ensuring that responses align with this personality.
Policy Agent
- Ensures all messages follow the communication policy of the bot, adding latency to responses.
Translator Agent
- Translates chatbot messages into the user's language automatically.
- To manually set the user's language, you can modify the
{{user.TranslatorAgent.language}}variable, using any "ISO 639-1" language code (e.g., en, fr, es).
Knowledge Agent
- Makes the chatbot answer questions based on Knowledge Bases.
- This agent searches for answers in the Knowledge Bases located in the same folder as the current workflow or in parent folders.
- The agent will only provide answers when the chatbot is on the Start Node or when the workflow is on a Capture Card that has Knowledge Bases enabled.
- To enable Knowledge Bases on a node, click the node in the workflow editor and enable the "Knowledge Bases" option in the right inspector panel.
Vision Agent
- Purpose: Extracts text content and descriptions from images in incoming messages.
- Uses GPT-4 Vision to extract content from images.
- The extracted content is stored in the
turn.VisionAgent.contentvariable for use in the conversation. - The message is also updated to include the extracted content in the "preview" field.
HITL (Human-in-the-Loop) Agent
- Allows the bot to escalate conversations to human agents for further assistance.
Botpress Features
Media
- Types of Media Supported: The bot supports text, images, and voice.
- Input Media: You can input text, images, and voice.
- Output Media: The bot can output text, images, and voice.
LLMs (Large Language Models)
Personal Models
Each workflow can have its own model, allowing for tailored responses.
Integrations
The bot supports various integrations with specific input and output types. Some examples include:
- OpenAI
- Dall-E Image Generation
- Google Analytics
- Calendly
- Jira
- Shopify
- Wikipedia
- Zendesk
- Trello
- Salesforce
- User-created private or public integrations are also supported.
Interfaces
Standard schema definitions for integrations, which act as LLM providers:
- Anthropic
- OpenAI
- Groq
Channels
The bot supports multiple channels for communication, including:
- Messenger
- Slack
Supported LLMs
The bot supports the following LLMs:
- GPT-4o (OpenAI)
- Claude 3.5 (Anthropic)
- Grok-1 (X)
- Cerebras
- Fireworks AI
- Hugging Face
Response Quality
You can choose the best model for higher-quality responses (e.g., GPT-4o) or a faster LLM (e.g., GPT-4o Mini).
Files API
- File Management: Allows for file uploads, downloads, and management of searchable documents.
- Knowledge Base Link: Files can be linked to the knowledge base, enabling the bot to answer questions based on these files.
- Supported Formats: The API supports both text and binary formats.
- Document Indexing: Documents can be indexed for efficient search and retrieval.
Training Botpress Model
The travel chatbot was trained using:
- Datasets: Utilizes datasets of existing tourism information from Banff/Waterton park.
- Official Tourism Sources: Uses information from official tourism sources, such as Parks Canada, for generating responses through retrieval-augmented generation (RAG).
- Advanced Prompting: Provides instructions within the Botpress builder to guide how the bot should respond in specific scenarios.